Area of Focus 2
GET THE PRESCRIPTION RIGHT FOR THE INDIVIDUAL PATIENT Detailed Results
If your facility struggles with individualizing prescriptions, you aren’t alone. Many providers and care teams struggle with understanding how to dose and the full range of options available for prescribing home hemodialysis. Some even believe the increased frequency of HHD prescriptions will not be of interest to a patient. However, clinical studies indicate patients who are prescribed 5 & 6 days a week experience a wide range of clinical and quality of life benefits.1,2
NxStage Connected Health data also indicates patients who treat 5 or 6 days per week are more likely not to miss a treatment compared with those who treat only 3 or 4 days per week.3
There are also other options available to meet patients’ needs such as nocturnal therapy performed overnight while the patient and care partner sleep and solo therapy performed by the patient during waking hours without a care partner.
If you haven’t discovered the NxStage Dosing Calculator make sure to take a look. When you input a patient’s vitals you are given a full suite of options to choose from that you can share with the full care team as well as the patient to select the option that is right for them.
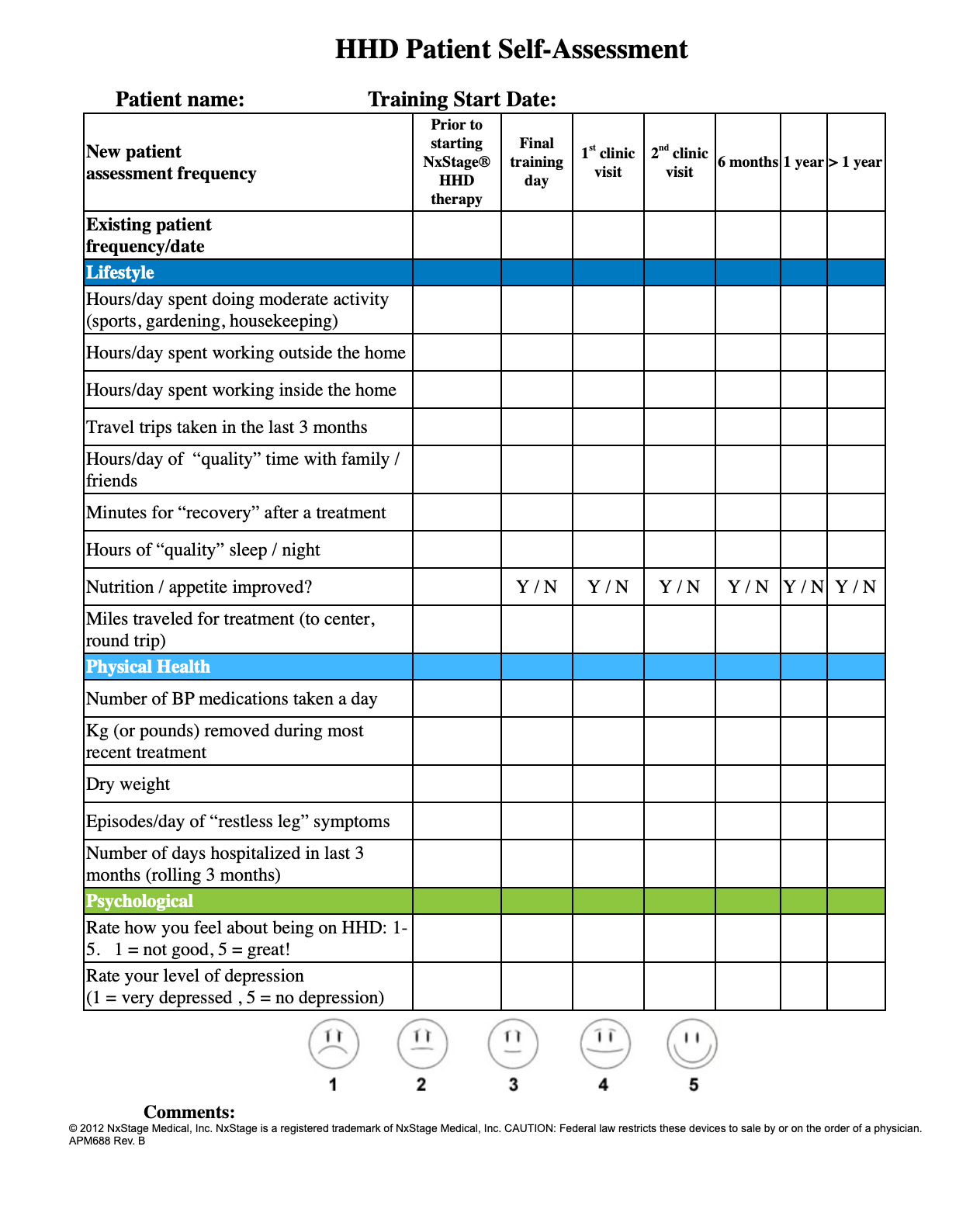
Below are a series of resources you can use to continue to have open conversations with your patients about their prescription as well as assess whether their prescription is still working for them. There are also a series of webinars available you can view to help understand the benefits and importance of proper dosing.
The reported benefits of home hemodialysis (HHD) may not be experienced by all patients.
The NxStage System is a prescription device and, like all medical devices, involves some risks. The risks associated with hemodialysis treatments in any environment include, but are not limited to, high blood pressure, fluid overload, low blood pressure, heart-related issues, and vascular access complications. When vascular access is exposed to more frequent use, infection of the site, and other access related complications may also be potential risks. The medical devices used in hemodialysis therapies may add additional risks including air entering the bloodstream, and blood loss due to clotting or accidental disconnection of the blood tubing set.
Home hemodialysis with the NxStage System during waking hours may not require a care partner, provided a physician and a qualified patient agree that solo home hemodialysis is appropriate. Patients performing nocturnal treatments are required to have a care partner. Care partners are trained on proper operation and how to get medical or technical help if needed.
Certain risks associated with hemodialysis treatment are increased when performing solo HHD because no one is present to help the patient respond to health emergencies. If patients experience needles coming out, blood loss, or very low blood pressure during solo HHD, they may lose consciousness or become physically unable to correct the health emergency. Losing consciousness or otherwise becoming impaired during any health emergency while alone could result in significant injury or death. Additional ancillary devices and training are required when performing solo HHD
Certain risks associated with hemodialysis treatment are increased when performing nocturnal therapy due to the length of treatment time and because therapy is performed while the patient and care partner are sleeping. These risks include, but are not limited to, blood access disconnects and blood loss during sleep, blood clotting due to slower blood flow and/or increased treatment time, and delayed response to alarms when waking from sleep.
Patients should consult their doctor to understand the risks and responsibilities of performing these therapies using the NxStage System.
References
- Kraus M, Finkelstein FO, Daoui R, et al. Short Daily Hemodialysis (SDHD) improves overall Quality of Life (QOL) and physical intimacy: interim results form the FREEDOM study. Abstract presented at the American Society of Nephrology Conference, 2011.
- Hall YN, Larive B, Painter P, et al. Effects of six versus three times per week hemodialysis on physical performance, health, and functioning: Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) randomized trials. Clim J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(5):782-794.
- Data on File. NxStage Medical, Inc. Nx2me Collections Information. 2019.